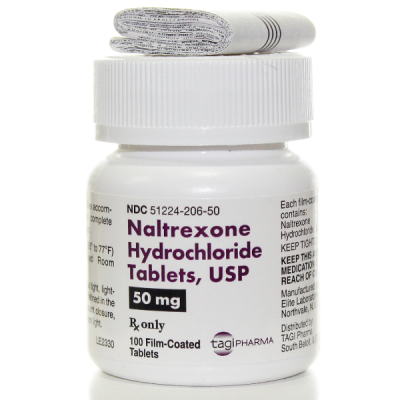
Naltrexone Tablets
$50.00 – $150.00
Naltrexone Tablets
Naltrexone is used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan to help individuals reduce alcohol consumption and prevent relapse in people who have stopped drinking.
SKU: N/A
Category: Pills
Naltrexone Tablets
Naltrexone is a medication primarily used to manage alcohol and opioid dependence. Here’s an overview of its description, uses, and warnings:
Description:
- Generic Name: Naltrexone
- Brand Names: Revia, Vivitrol
- Drug Class: Opioid antagonist
- Form: Tablets (available in various strengths) and extended-release injectable suspension
Uses:
- Alcohol Dependence: Naltrexone is used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan to help individuals reduce alcohol consumption and prevent relapse in people who have stopped drinking.
- Opioid Dependence: It is also used to help people with opioid dependence by blocking the effects of opioids and reducing cravings, thus supporting efforts towards recovery.
- Off-label Uses: Naltrexone may also be used off-label for conditions like fibromyalgia, certain autoimmune disorders, and impulse control disorders, although its effectiveness for these purposes may vary.
Warning:
- Opioid Withdrawal: Before starting naltrexone treatment, individuals must be opioid-free for a minimum of 7-10 days to avoid precipitating withdrawal symptoms. Using opioids while on naltrexone can lead to sudden opioid withdrawal symptoms, which can be severe.
- Liver Function: Naltrexone may cause liver damage, particularly at high doses. Liver function should be monitored before starting treatment and periodically throughout.
- Contraindications: Naltrexone should not be used in individuals with acute hepatitis or liver failure. It should also be avoided in people who are currently using opioids or undergoing opioid withdrawal.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: The safety of naltrexone during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well-established. It is generally avoided during pregnancy unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks, and caution is exercised during breastfeeding.
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, fatigue, and insomnia. Some individuals may experience mood changes, anxiety, or irritability.
- Overdose Risk: As an opioid antagonist, high doses of naltrexone can block the effects of opioids, potentially leading to overdose if an individual relapses and takes opioids in large amounts.
- Interactions: Naltrexone may interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect liver enzymes or involve opioid receptors. It’s important to inform your doctor of all medications and supplements you are taking before starting naltrexone.
Dosage:
- The dosage of naltrexone may vary depending on the individual’s condition and response to treatment. It’s important to follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication, including naltrexone, and discuss any concerns or questions you may have about its use and potential risks.
| Amount | 100 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills |
|---|
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.
Related products
Pills
$100.00 – $230.00
Pills
$50.00 – $150.00
Pills
$150.00 – $800.00
Pills
$100.00 – $250.00
Pills
$50.00 – $150.00
Pills
$50.00 – $150.00
Hallucinogens
$300.00 – $700.00
Hallucinogens
$100.00 – $250.00






Be the first to review “Naltrexone Tablets”