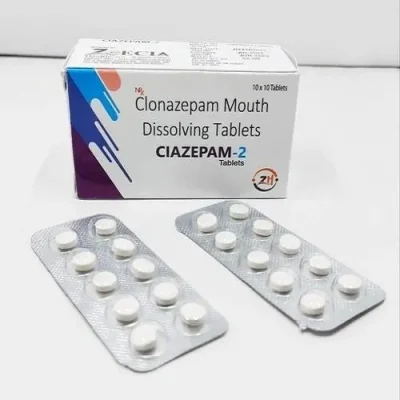
Clonazepam Tablets
$110.00 – $600.00
Clonazepam Tablets
Clonazepam is a benzodiazepine medication primarily used to treat certain seizure disorders (such as epilepsy) and panic disorders with or without agoraphobia.
It is also prescribed off-label for other conditions such as anxiety disorders and certain types of insomnia, though its long-term use for these purposes is generally discouraged due to the risk of dependence and tolerance.
Clonazepam Tablets
Clonazepam is a benzodiazepine medication primarily used to treat certain seizure disorders (such as epilepsy) and panic disorders with or without agoraphobia.
It is also prescribed off-label for other conditions such as anxiety disorders and certain types of insomnia, though its long-term use for these purposes is generally discouraged due to the risk of dependence and tolerance.
Here are some key points about clonazepam tablets:
- Mechanism of Action: Clonazepam works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits the activity of neurons in the brain. By increasing GABA activity, clonazepam has a calming effect on the central nervous system, which can help reduce seizures and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and panic.
- Seizure Disorders: Clonazepam is commonly prescribed as an adjunctive treatment for certain types of seizures, including absence seizures and myoclonic seizures. It may also be used for the management of status epilepticus, a life-threatening condition characterized by prolonged or recurring seizures.
- Panic Disorder: Clonazepam is FDA-approved for the treatment of panic disorder, a type of anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent panic attacks. It can help reduce the frequency and severity of panic attacks and may also alleviate associated symptoms such as anticipatory anxiety and phobic avoidance.
- Dosage: Clonazepam tablets come in various strengths, typically ranging from 0.5 mg to 2 mg. The dosage prescribed depends on the condition being treated, its severity, and individual factors such as age and medical history. It’s important to take clonazepam exactly as prescribed by your doctor and to avoid sudden changes in dosage without medical supervision.
- Side Effects: Common side effects of clonazepam may include drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, impaired coordination, and memory impairment. It may also cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and constipation. Long-term use of clonazepam can lead to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms if discontinued abruptly.
- Precautions: Clonazepam should be used with caution in individuals with a history of substance abuse or addiction, as it has the potential for abuse and dependence. It should also be used cautiously in elderly patients and those with respiratory conditions, as it can cause respiratory depression, especially at higher doses.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Clonazepam may pose risks to the fetus if used during pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester. It can also pass into breast milk and may cause sedation or other adverse effects in nursing infants. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should discuss the risks and benefits of clonazepam with their healthcare provider.
If you have any questions or concerns about clonazepam or its use, it’s important to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual medical history and the specific circumstances of your treatment.
| Amount | 100 pills, 200 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills |
|---|
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.
Related products
Pills
Pills
Pills
Pills
Hallucinogens
Pills
Pills







Be the first to review “Clonazepam Tablets”